Xin chào anh em, trong bài viết này xin chia sẻ với anh em một chút về đồng crypto mới nổi gần đây mang tên Pi Network. Mình sẽ làm rõ cho anh em hiểu bản chất của Pi Network có phải lừa đảo không để anh em đỡ tốn công tốn sức tìm hiểu, đắn đo.
Vào việc luôn nhé!
Đầu tiên, Pi Network là gì?
Theo những gì được công bố thì Pi Network là loại tiền ảo chỉ khai thác được bằng thiết bị di động. Pi được quảng cáo là khai thác mà không tốn tài nguyên thiết bị, không mất tiền dữ liệu mạng, chỉ cần bạn bật app điểm danh hàng ngày.
Pi được thành lập bởi một đội ngũ cựu sinh viên Đại học Stanford danh tiếng. Trong đó bao gồm 2 tiến sĩ và một MBA. Tuy vậy, khác với những dự án khác, các sáng lập viên của Pi rất ít khi xuất hiện để công bố các thông tin về dự án cũng như các hoạt động khác. Đây là một điều khá bất thường.
Khai thác Pi rất đơn giản, bạn chỉ cần tải ứng dụng Pi Network về sau đó đăng ký tài khoản cũng rất đơn giản. Đăng ký xong bạn chỉ cần nhấn Start để bắt đầu đào Pi, quá trình đào diễn ra ngay cả khi ngắt kết nối internet và không làm hao pin, không sử dụng dữ liệu mạng. Điều bạn cần làm chỉ là mở ứng dụng mỗi 24 giờ để “điểm danh”.
Tốc độ khai thác Pi sẽ giảm dần khi số lượng người tham gia đào tăng lên. Nhưng có một điều khá hay ho là nếu mời người khác tham gia mạng con cùng với bạn thì tốc độ đào sẽ tăng lên. Nghe quen quen :)
Bạn được gì và mất gì khi đào Pi?
Ở thời điểm hiện tại, thứ mà bạn nhận được khi đào Pi chỉ là những lời hứa, những ảo mộng giàu sang trong tương lai.
Còn những thứ bạn mất gồm:
- Công sức lôi kéo người khác cùng đào Pi
- Tốn tiền điện sạc smartphone để đào Pi
- Tốn tài nguyên của smartphone
- Mất thông tin, dữ liệu nhạy cảm trên máy
- Mất niềm tin vào công nghệ blockchain
- Mất công sức vào một đồng tiền ảo không có giá trị
- Mất uy tín với những người xung quanh
- Sau này còn có thể mất tiền nếu đồng Pi yêu cầu bạn đồng thuận về giá, đặt cho Pi một giá trị nào đó rồi bắt mỗi người tham gia phải mua 1 Pi với giá đồng thuận để chứng minh sự ủng hộ.
Các dẫn chứng cho thấy Pi là một đồng tiền ảo lừa đảo
Đầu tiên, chẳng có một đồng tiền ảo nào khai thác đơn giản như Pi. Việc đào tiền ảo không dễ dàng như các bạn nghĩ. Tất cả các thợ mỏ thời 4.0 đều phải đầu tư rất nhiều tiền cho dàn máy, kết nối mạng để đào tiền ảo, cạnh tranh với các thợ mỏ khác. Họ đào bằng cách xác thực giao dịch theo các khối, mỗi lần xác thực thành công thợ mỏ sẽ được trả thưởng bằng tiền ảo.
Nói chung, đào tiền ảo theo cách điểm danh 24 giờ một lần là xong thì chỉ có Pi mà thôi.
Thứ hai, Pi không công bố công nghệ lõi, giấu kín mã nguồn. Mọi dự án blockchain, tiền ảo đều theo nguyên tắc minh bạch. Ngay cả Bitcoin, ETH cũng phải công khai mã nguồn để thể hiện tính phi tập trung vậy mà Pi lại không. Pi có công nghệ lõi mà không công bố hay chả có cái lõi nào chỉ giỏi nổ thì chúng tôi không dám kết luận. Tuy nhiên, một dự án tiền ảo uy tín thì chắc chắn phải công bố công nghệ lõi.
Thứ ba, Pi không công bố các mốc thời gian cụ thể của các giai đoạn phát triển. Mặc dù trong sách trắng, Pi cũng bày ra ba giai đoạn Thiết kế, thử nghiệm trên Testnet và giai đoạn chính trên Mainnet. Tuy nhiên mốc thời gian cụ thể của từng giai đoạn thì lại chẳng thấy đâu.
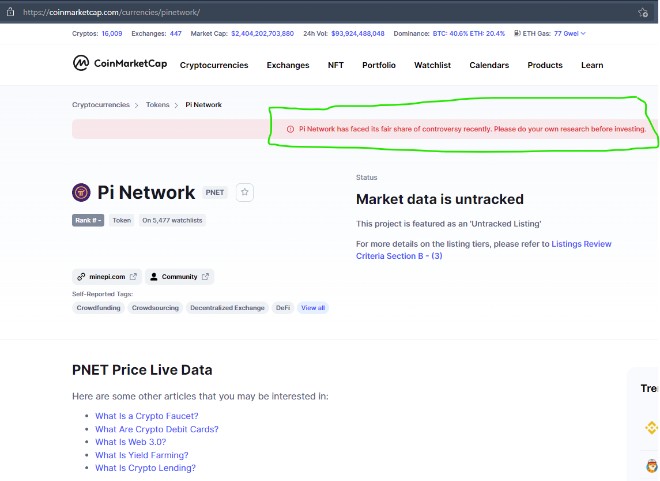
Thứ tư, Pi bị sàn giao dịch tiền ảo CoinMarketCap gắn mác là gây tranh cãi, nhà đầu tư cân nhắc trước khi xuống tiền.
Thứ năm, một số tên miền của Pi bị đưa vào danh sách đen hoặc bị cảnh báo bởi các phần mềm chống virus như Virus Total, Microsoft Edge SmartScreen….
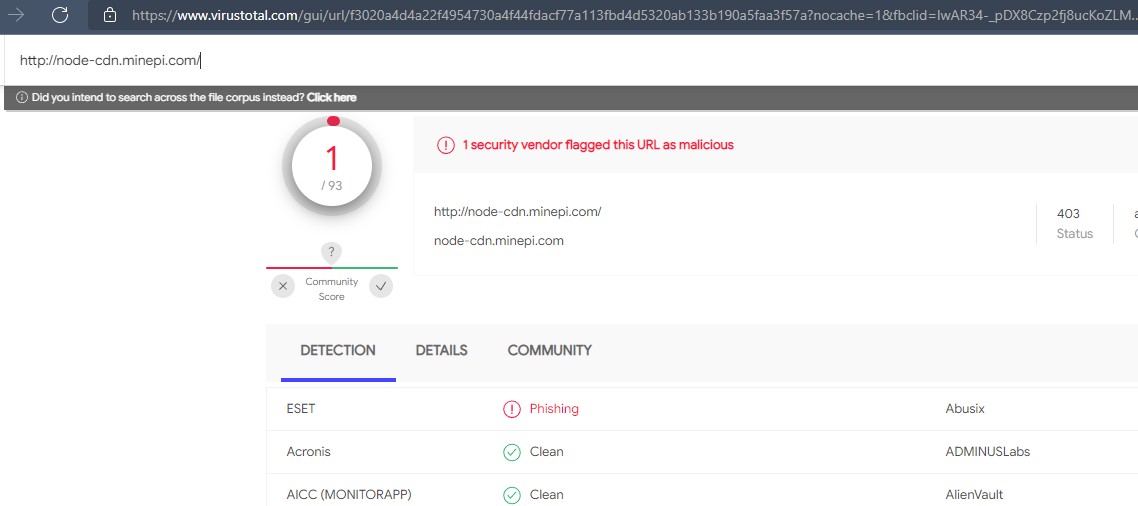
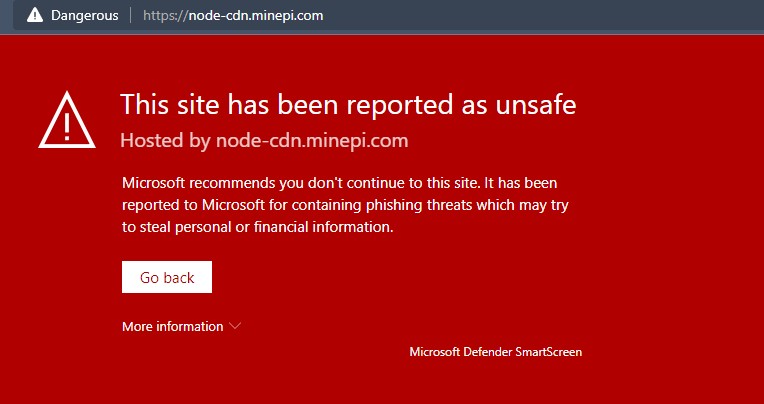
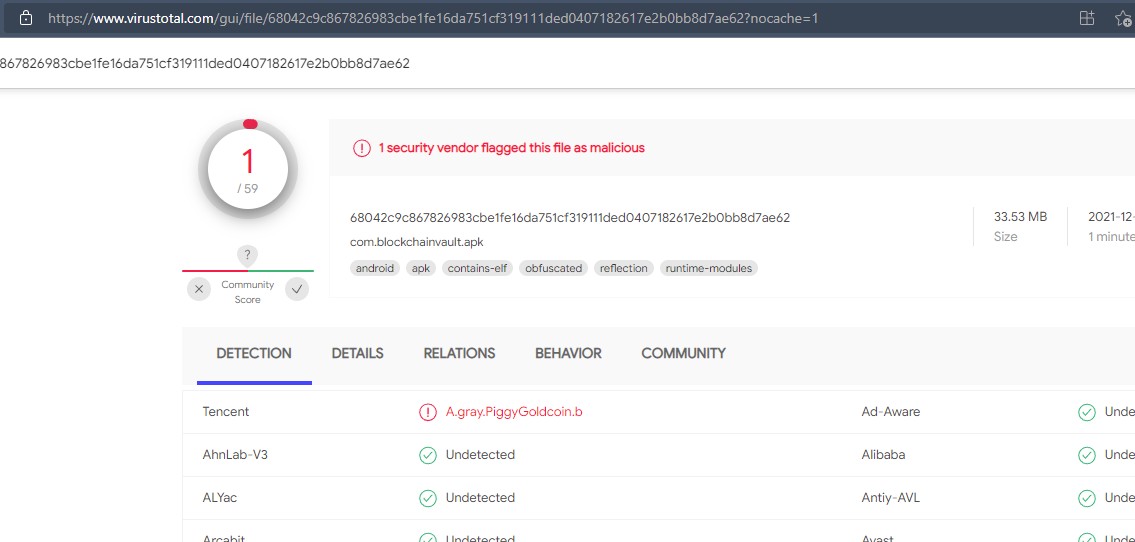
Thứ sáu, ngay cả ứng dụng Pi Network cũng bị Tencent đưa vào danh sách nguy hiểm.
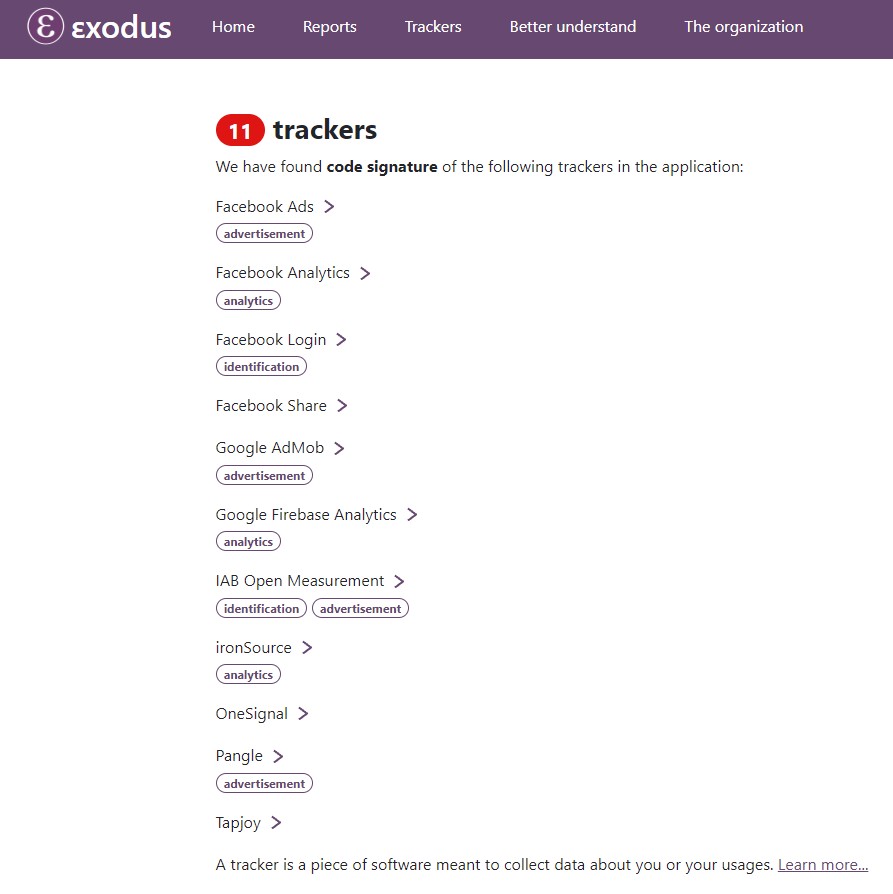
Thứ bảy, Pi Network yêu cầu quá nhiều quyền nhạy cảm. Theo nghiên cứu của Exodus, ứng dụng Pi Network dùng tới 11 tracker để thu thập dữ liệu người dùng phục vụ cho mục đích quảng cáo. Nghiêm trọng hơn, chỉ là một ứng dụng đào tiền ảo nhưng Pi yêu cầu tới 28 quyền truy cập bao gồm các quyền vô lý như đọc danh bạ, xem thông tin mạng, sử dụng phần cứng sinh trắc học, sử dụng phần cứng vân tay, kiểm soát trạng thái mạng…
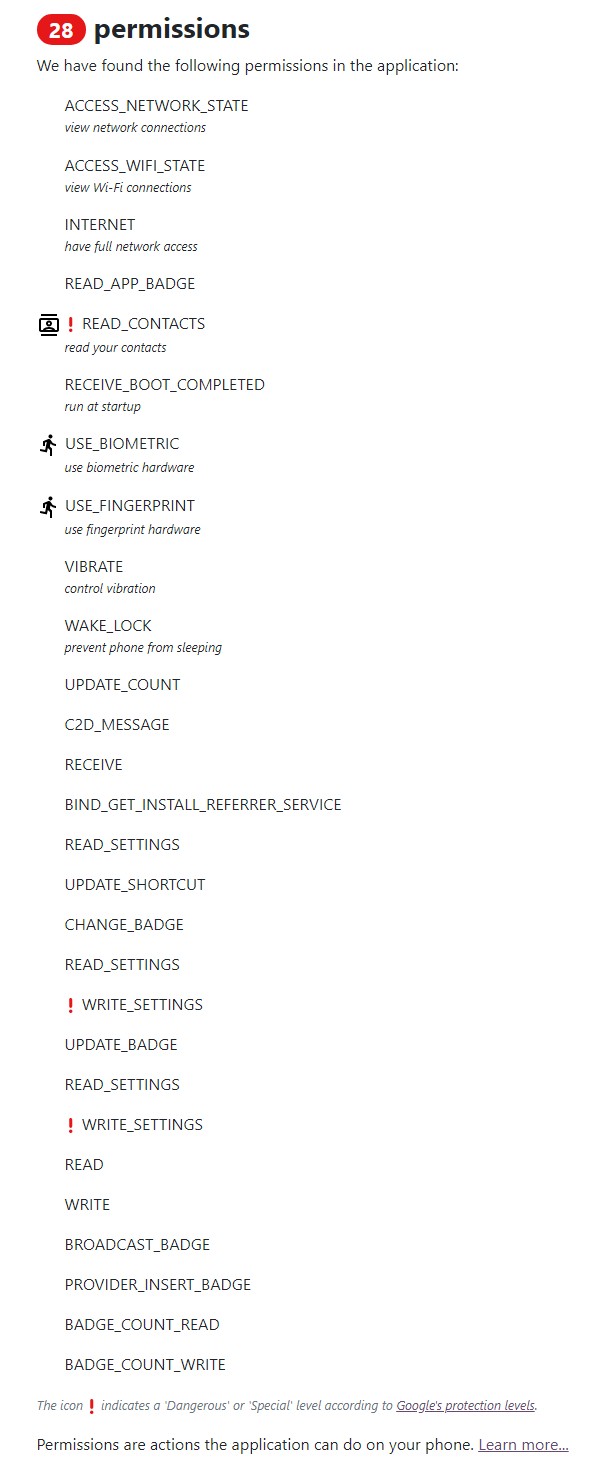
Thứ tám, nhiều chuyên gia đã lên tiếng cảnh báo về việc Pi Network không an toàn với người dùng. Thậm chí, Pi còn bị cho là một mô hình lừa đảo đa cấp.
Thứ chín, theo Wjbuboiz một nhóm chuyên về bảo mật có sự tham gia của Hiếu PC, thì Pi chả có cái gì gọi là blockchain. Ngay cả ứng dụng Pi Network cũng không phải là một app tử tế mà chỉ là một webview. Còn theo Wibugirl thì quá trình đào Pi mà những “người tiên phong” đang thấy chỉ là Javascirpt timer. Tất cả những số PI đang chạy mà các bạn thấy trên màn hình không phải là app PI đang đào coin hay chạy blockchain gì cả mà chỉ là họ setinterval trong Javascript code để thay đổi giá trị PI trên UI mà thôi
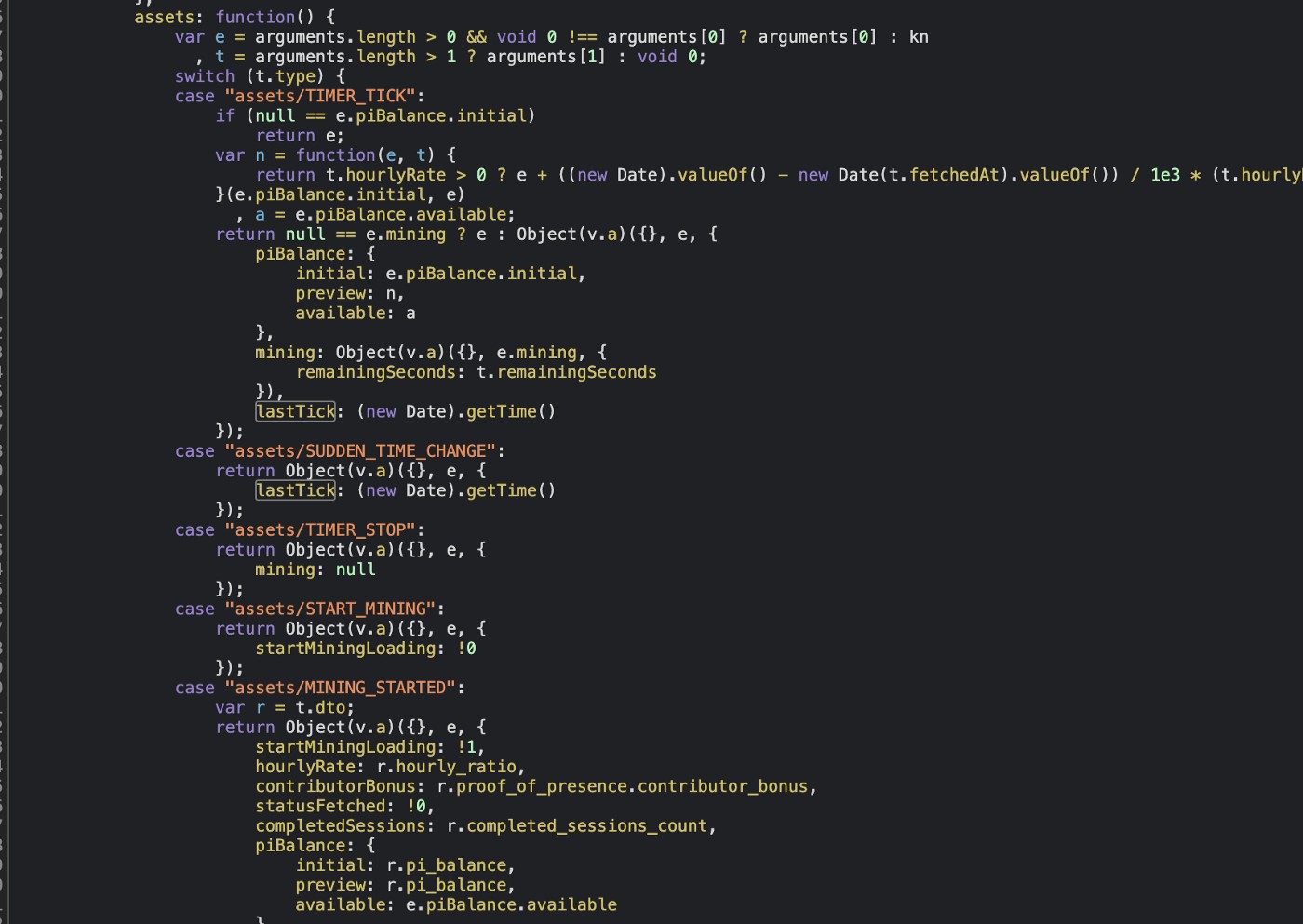
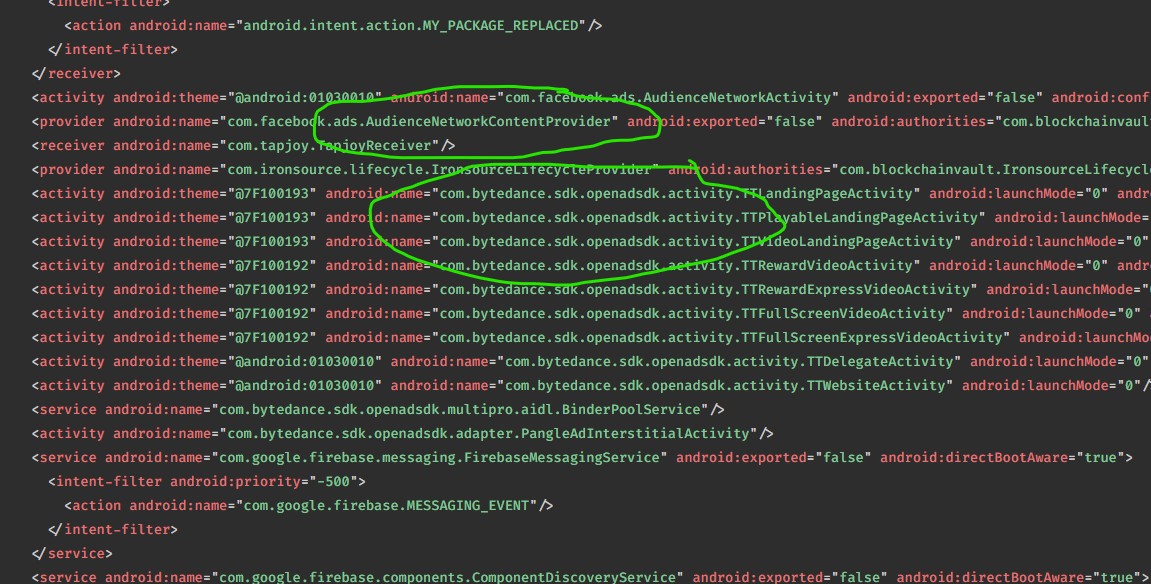
Thứ mười, tất nhiều đoạn code trong app Pi dành riêng cho việc chạy quảng cáo.
Tương lai của Pi Network
Rồi, tới đây nhiều bạn sẽ hỏi là tôi chưa thấy Pi lừa đảo gì tôi cả. Vậy thì chúng ta sẽ nói thêm một chút về tương lai của Pi. Đoạn này tôi mượn ý tưởng của một anh bạn, một chuyên gia về công nghệ và tiền ảo.
Đúng như phản biện mà các bạn đưa ra, hiện tại Pi chưa lừa đảo ai cả. Những kẻ đứng đằng sau đồng tiền ảo này hiện tại chỉ cần ngồi rung đùi ăn tiền quảng cáo cũng đủ rồi không cần lừa ai làm gì nữa. Thế nhưng cứ như vậy mãi, cứ đào mãi mà chẳng mua bán, chẳng ứng dụng được gì thì cũng không ổn.
Vì thế, để hốt cú chót những kẻ đứng đằng sau Pi sẽ tạo ra một đồng token Pi Network thật sự. Với cơ chế đồng thuận về giá tự nhận từ trước, mấy anh sẽ yêu cầu những “người tiên phong” phải đồng thuận một mức giá khởi điểm dành cho Pi (ví dụ 100 USD/1 Pi) và đề nghị mỗi người phải bỏ tiền ra mua 1 Pi coi như chứng minh sự ủng hộ. Vì là đồng thuận nên nếu muốn bán được Pi với giá 100 USD thì anh phải là người chấp nhận mua 1 Pi với giá 100 USD, hợp lý chưa.
Nhưng mà ban đầu, các giao dịch sẽ ở dạng chỉ được mua chứ không cho bán. Khi có trong tay hàng nghìn, hàng triệu Pi thì chắc chắn nhiều người sẽ không tiếc việc bỏ 100 USD ra mua một Pi. Ờ thì mất có một đồng, sau này bán hàng ngàn đồng với giá 100 USD hoặc chỉ cần 50 USD cũng lãi to rồi.
Với số lượng “người tiên phong” đào Pi lên tới hàng chục triệu chỉ cần vài % đồng ý bỏ 100 USD mua Pi là những kẻ đứng sau giàu sụ rồi. Tiếp theo chúng sẽ cao chạy xa bay, giá Pi bao nhiêu không còn quan trọng nữa, cộng đồng tự sinh tự diệt… Khi đó, bạn sẽ thấy Pi Network lừa đảo bạn như thế nào.
Thôi để chốt lại mình xin dẫn một câu của anh chàng chuyên nói đạo lý trên mạng: Trên đời này có làm thì mới có ăn…